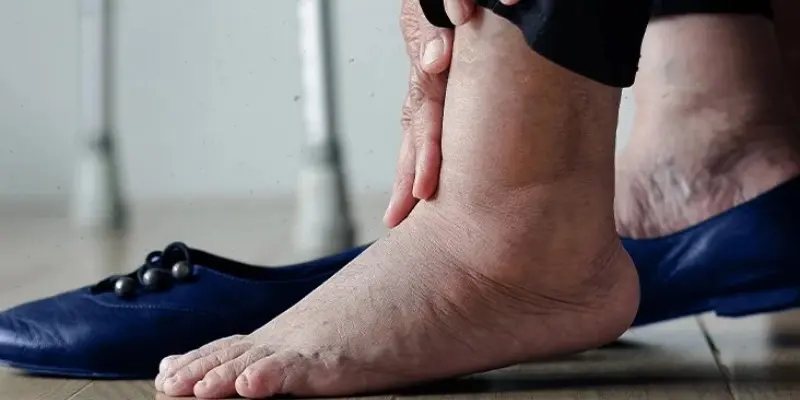
Diabetes is a chronic illness that affects the body’s ability to process sugar, resulting in high blood glucose (sugar) levels. Over time, these high glucose levels can lead to a wide range of health complications, many of which can manifest in the legs.
Recognizing India Travel News early and managing diabetes effectively can prevent adverse effects and improve quality of life.
1. Peripheral Neuropathy
The most common leg-related symptom in individuals with diabetes is peripheral neuropathy, a type of nerve damage caused by chronically high blood sugar levels.
Up to 50% of people with diabetes will develop neuropathy, with the majority experiencing symptoms in their legs and feet. The symptoms of peripheral neuropathy often start slowly and progress over time. These can include:
- Pain and Sensitivity: People with diabetic neuropathy may experience pain or discomfort in their legs and feet, including burning, stabbing, or shooting pains. Even the sensation of clothing against the skin may cause discomfort.
- Numbness and Tingling: Numbness or reduced sensation in the legs and feet is another common symptom. This can often start at the tips of the toes and gradually spread upwards. People may also experience feelings of tingling or ‘pins and needles’.
- Muscle Weakness: Neuropathy can lead to muscle weakness, making it difficult to walk or maintain balance.
- Loss of Reflexes: Particularly in the ankles, diminished reflexes can occur.
It’s important to note that peripheral neuropathy can lead to a loss of sensation in the legs and feet. As a result, people might not notice minor injuries such as cuts or blisters, which can progress to more serious infections if not treated promptly.
2. Peripheral Artery Disease (PAD)
Diabetes also increases the risk of peripheral artery disease (PAD), a condition in which the blood vessels in the legs are narrowed or blocked due to fatty deposits. This can reduce blood flow to the legs and feet, leading to a range of symptoms:
- Intermittent Claudication: This term refers to leg pain or discomfort that occurs when walking or exercising because the muscles are not getting enough blood. The pain usually eases with rest.
- Coldness and Color Changes: The affected leg or foot may feel cooler to the touch, and there may be noticeable color changes due to the reduced blood flow.
- Slower Healing: Wounds or sores on the feet or legs heal slower due to diminished blood flow.
- Loss of Hair or Delayed Hair Growth: Reduced blood flow can also affect hair growth on the legs.
- Pulse Changes: It may be difficult to feel a pulse in the feet or the pulse may be weaker than usual.
3. Skin Changes
Over time, diabetes can cause changes to the skin on the legs. These can include:
- Dry Skin: High blood glucose levels can cause the body to lose fluid, leading to dry, itchy skin.
- Skin Discoloration: A condition known as diabetic dermopathy can cause light brown, scaly patches on the skin, particularly on the front of the legs.
- Skin Infections: People with diabetes are more prone to various skin infections, including bacterial and fungal infections.
- Acanthosis Nigricans: This condition is characterized by areas of darkened, velvety skin, often on the back of the neck, but it can also appear on the legs.
Related Topics: Top Places to Visit in Kolkata
4. Foot Problems
A range of foot problems are common in people with diabetes. These can include:
- Fungal Infections: Diabetes can make individuals more prone to fungal infections, such as athlete’s foot.
- Foot Ulcers: An ulcer is a sore that goes through the skin and into the flesh beneath. Foot ulcers can develop from minor scrapes or cuts that heal slowly, or from the friction of shoes that don’t fit well.
- Charcot Foot: This is a serious condition that can cause the foot to become deformed. It occurs due to nerve damage and poor blood flow.
While these symptoms may seem daunting, they underline the importance of regular foot care, prompt treatment of foot problems, and good glycemic control for people with diabetes. Many of these symptoms can be managed or even prevented with appropriate care and medical attention.
As with any health concern, early detection is key, and individuals who notice any of these symptoms should consult a healthcare professional promptly. Regular check-ups and keeping blood sugar levels under control can also help to prevent or manage these leg-related symptoms of diabetes.